E-mail: info@solidecking.com
tel-phone:86-21-63803633
Address:Room 103, Jinfeng Building, No. 31 Hengfeng Road, Jing'an District, Shanghai
Mobile phone:13816755915 ©2016 Leshang Technologies Co., Ltd.
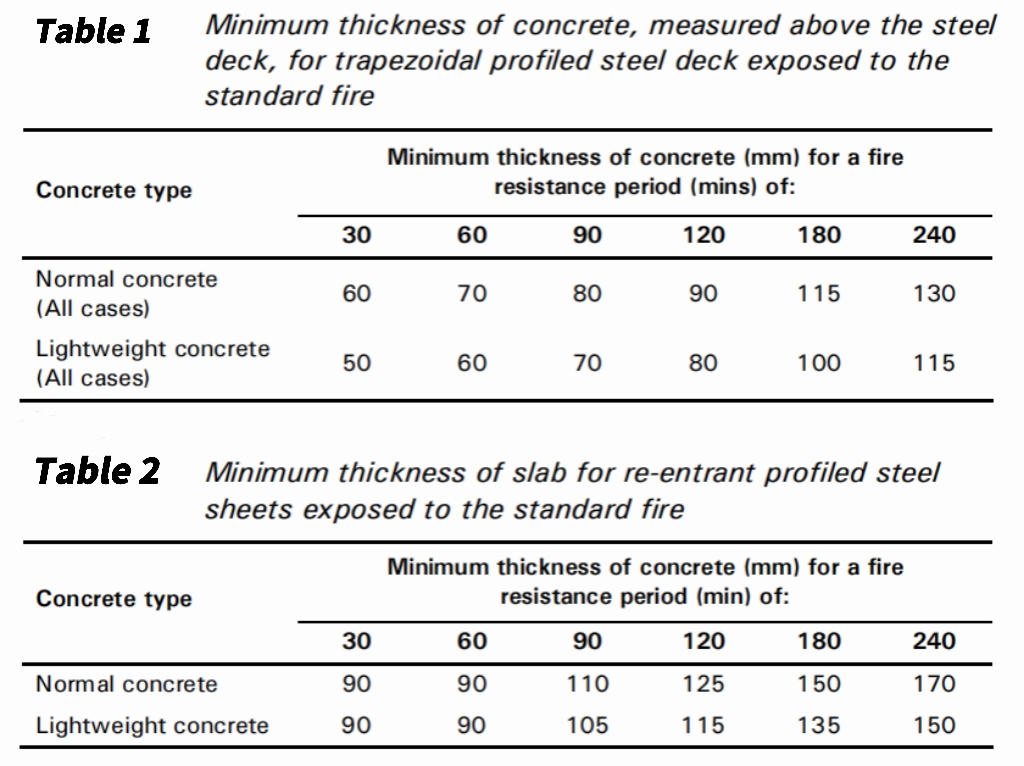
The insulation criterion is satisfied by providing adequate slab thickness to ensure that the temperature of the unexposed surface of the slab does not exceed 140o C. BS 5950-8 and the UK National Annex to EN1994-1-2 provide a table of recommended concrete thicknesses to satisfy the insulation criterion for common periods of fire resistance. The minimum thickness of concrete required to satisfy the insulation requirements is shown in Table 1 for trapezoidal decks and Table 2for re-entrant decks. Figure 3 shows that the insulation depth depends on the type of profile, and it is the concrete cover to the main crest of the deck for trapezoidal profiles and the full slab depth for re-entrant profiles.
EN1994-1-2 permits the designer to calculate the bending resistance and insulation properties assuming that composite slabs fulfil the integrity criterion. Fire tests have been carried out on slabs with conventional fabric reinforcement, and on fibre reinforced slabs.
The load bearing resistance of the slab at elevated temperatures can be determined by calculation in accordance with the principles given in EN1994-1- 2. The UK National Annex provides additional guidance on determining design temperatures for UK steel decking geometries.
Depending on the span required, an increased size of fabric may need to be used, or extra bars may need to be placed in the troughs of the deck, to satisfy the load bearing criteria (R) for the fire condition. In either case, the additional reinforcement is used to compensate for the loss of strength of the (exposed) decking at elevated temperatures. Design guidance covering this aspect is normally given by the steel decking manufacturers in their design tables. These design tables are based on the extended application of fire test results and provide product specific guidance which will result in the most economic solutions for fire design. The extended applications of the fire test results are based on a design model for plastic resistance that is in accordance with the principles of EN1994-1-2 §4.3.1 and the recommendations of the UK National Annex to EN1994-1-2.
In the UK National Annex, the use of Informative Annex D of EN1994-1-2 is rejected as many UK decking profiles are outside the limits of the field of application. It was found that when the methods in Annex D were applied to these decking geometries, unusable answers were obtained. For projects in other European countries where the use of Annex D is recommended, it is likely that the manufacturer’s fire design tables will be the only valid method of design for UK decking profiles.
Slab designs that comply with the recommendations of EN1994-1-1 for room temperature design are deemed to have 30 minutes fire resistance, when assessed under the load bearing criteria ‘R’, but these slabs still need to be checked for compliance with the insulation criteria.
E-mail: info@solidecking.com
tel-phone:86-21-63803633
Address:Room 103, Jinfeng Building, No. 31 Hengfeng Road, Jing'an District, Shanghai
Mobile phone:13816755915 ©2016 Leshang Technologies Co., Ltd.
